Understanding Cardiovascular Diseases
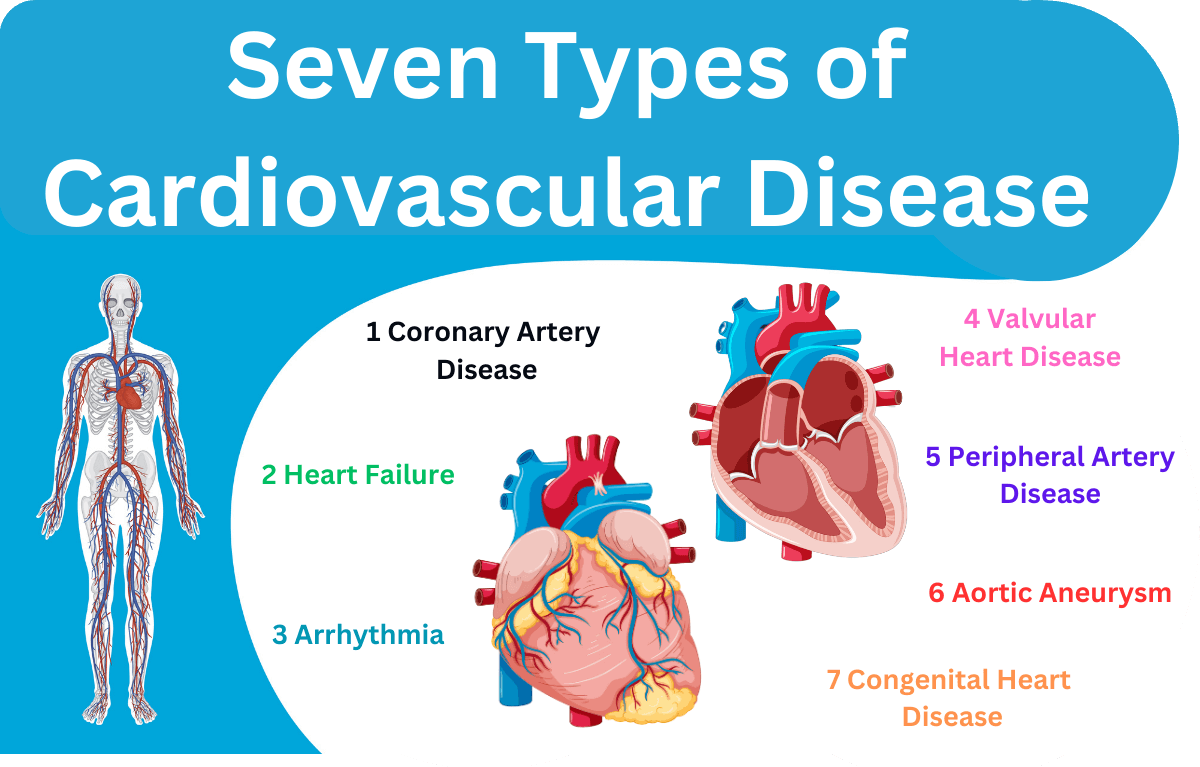
What are Cardiovascular Diseases?
Cardiovascular diseases encompass a range of disorders affecting the heart and blood vessels. The primary types include:
-
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): The narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries.
-
Stroke: A condition where the blood supply to the brain is interrupted or reduced.
-
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Narrowing of the peripheral arteries, typically in the legs.
-
Heart Failure: A condition where the heart cannot pump blood effectively.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of CVDs. These include:
-
High Blood Pressure: Puts excessive strain on blood vessels.
-
High Cholesterol Levels: Leads to plaque buildup in arteries.
-
Smoking: Damages the blood vessels and heart.
-
Diabetes: Increases the risk of heart disease.
-
Obesity: Contributes to other risk factors like hypertension and diabetes.
-
Physical Inactivity: Leads to poor cardiovascular fitness.
-
Unhealthy Diet: High in saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium.
Preventive Measures for Cardiovascular Diseases
Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial in preventing CVDs. Key lifestyle changes include:
Healthy Eating:
-
Increase Intake of Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for at least five servings daily.
-
Choose Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains over refined grains.
-
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: These fats are found in fried foods, baked goods, and processed snacks.
-
Reduce Sodium Intake: Aim for less than 2,300 mg per day.
Regular Physical Activity:
-
Aerobic Exercises: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week (e.g., brisk walking, cycling).
-
Strength Training: Perform muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
-
Body Mass Index (BMI): Keep BMI within the range of 18.5-24.9.
Quit Smoking:
-
Support Programs: Utilize smoking cessation programs and resources.
Medical Interventions
In some cases, medical intervention is necessary to manage risk factors effectively:
Medications:
-
Statins: Help lower cholesterol levels.
-
Antihypertensives: Control high blood pressure.
-
Antidiabetic Medications: Manage blood sugar levels.
Regular Health Screenings:
-
Blood Pressure Checks: Monitor regularly.
-
Cholesterol Levels: Get tested every 4-6 years.
-
Diabetes Screening: Regular testing for at-risk individuals.
Prevalence of Cardiovascular Diseases
|
Region
|
Prevalence (%)
|
Leading Cause of Death (%)
|
|
North America
|
11.0
|
30.0
|
|
Europe
|
10.5
|
29.0
|
|
Asia
|
8.0
|
25.0
|
|
Africa
|
5.5
|
20.0
|
|
South America
|
6.5
|
23.0
|
Source: World Health Organization (WHO), 2023
Q&A
Q: What is the most common cause of cardiovascular diseases?
A: The most common cause is atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) inside the arteries, leading to reduced blood flow.
Q: How often should one get screened for cardiovascular risk factors?
A: Adults should have their blood pressure checked at least once every two years, cholesterol levels every 4-6 years, and diabetes screenings based on individual risk factors and family history.
Q: Can lifestyle changes alone prevent cardiovascular diseases?
A: While lifestyle changes significantly reduce the risk, some individuals may require medication to manage existing conditions such as hypertension, high cholesterol, or diabetes.
